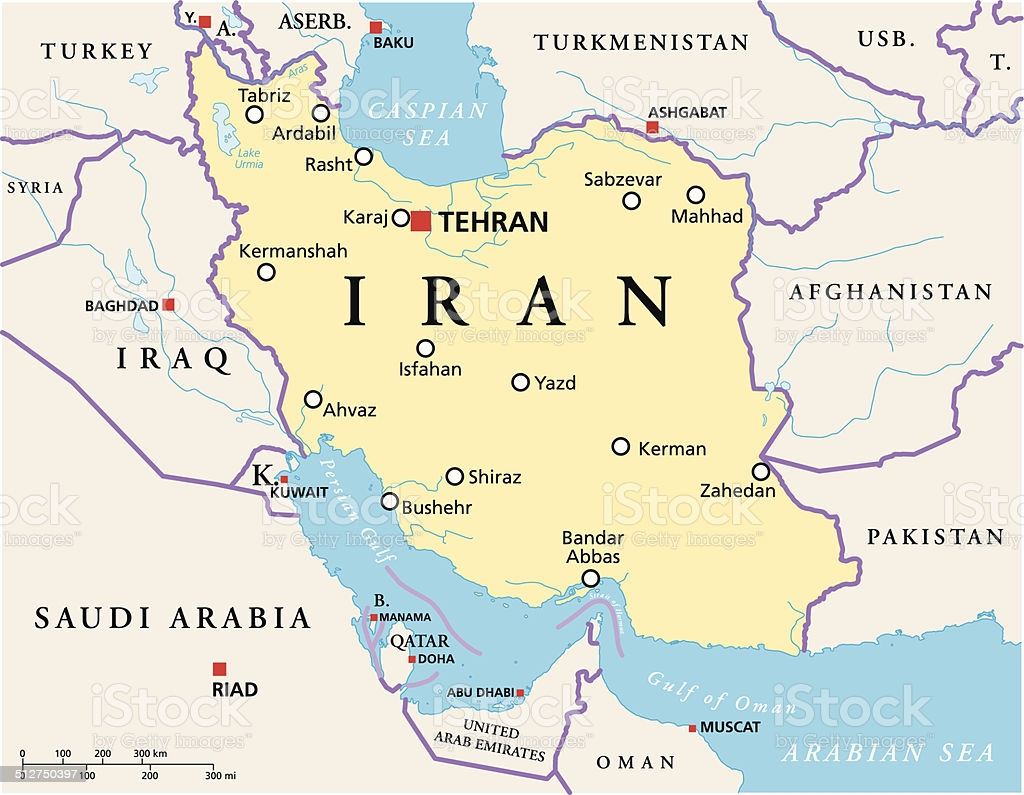
A mountainous, arid, and ethnically diverse country in southwest Asia. Most of Iran consists of the central desert plateau, which is surrounded by high mountains and is accessed through highways. Its capital is Tehran, a large metropolis located on the southern slopes of the Alborz Mountains.
Iran Political Map with capital Tehran, national borders, most important cities, rivers and lakes. English labeling and scaling. Illustration.
The city, known for its beautiful architecture and lush gardens, was partially destroyed in the decades after the Iranian Revolution in 1978-1979, although efforts were later made to preserve the monuments and expand the city’s network of parks. Like Tehran, cities like Isfahan and Shiraz combine modern buildings with important landmarks of the past and act as major centres of education, culture and commerce.
The heart of the ancient Iranian empire, Iran has long played an important role in the region as an imperial power and later due to its strategic location and abundant natural resources, especially oil, has been considered a factor for colonial rivalries and superpowers. The roots of this country as a distinct culture and society date back to the Achaemenid period, which began in 550 BC. Since then, what is now Iran – traditionally known as Persia. The conquest of Persia by the Muslim Arabs in the seventh century AD had the most lasting impact because Iranian culture was completely conquered by its conquerors.
The cultural renaissance of Iran in the late eighth century led to the revival of Persian literary culture. In the following centuries, with the emergence of the rule of the Shiite clergy based in Persia, a combination was formed between the culture of Iran and Shiite Islam, each of which was indelible with the other tincture. Towards the end of the Qajar period, the country’s problems led to the rise of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1925, whose unplanned efforts to modernize Iran led to widespread dissatisfaction and the subsequent overthrow of the dynasty in 1979 revolution. Islamic Republic A parliamentary democracy with an Islamic religious government run by the country’s clerics.
Iran’s economy has sectors of hydrocarbons, agriculture and services, as well as a significant government presence in production and financial services. Iran ranks second in the world in terms of natural gas reserves and fourth in terms of crude oil reserves, and although it is relatively diverse for an oil-exporting country, economic activities and government revenues still rely on oil revenues and are therefore volatile.
GDP in the Iranian calendar 2020/21 is estimated at 628 billion dollars, which is calculated at the official exchange rate for a population of about 84 million people. Iran’s real GDP will increase by 1.7% in 2020/21. COVID-19 production declined less than other countries, as Iran’s economy shrank 12% in the past two years. The economic recovery in the third and fourth quarters of 2020 was much higher than expected, both in the oil and non-oil sectors, with a jump in the non-oil sector due to production, as lower exchange rates made domestic production more competitive.
